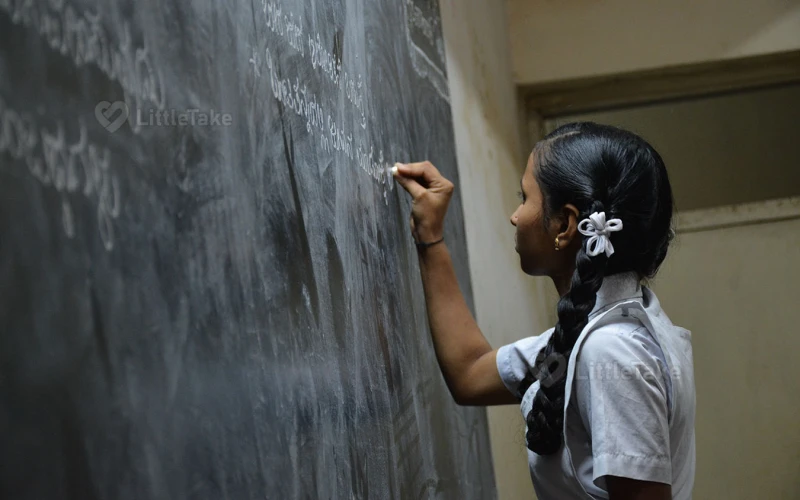
Rural Education in India
Rural education is a critical aspect of India's education system, as a significant proportion of the population resides in rural areas. This article discusses the challenges and initiatives associated with rural education in the country.
1. Challenges in Rural Education
- Lack of access to quality education due to inadequate infrastructure, insufficient teachers, and limited resources.
- Higher dropout rates, particularly among girls, due to socio-economic factors and cultural barriers.
- Language barriers and low levels of parental education impacting students' learning outcomes.
2. Government Initiatives
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) aims to provide universal access to primary education in rural areas.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) focuses on improving the quality of secondary education in rural areas.
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme provides nutritious meals to students in government schools, encouraging enrollment and retention.
3. Role of NGOs and Community Participation
- NGOs play a crucial role in supplementing government efforts to improve rural education, by adopting schools, providing teacher training, and offering learning resources.
- Community participation is essential for creating awareness and ensuring the sustainability of rural education initiatives.
- Public-private partnerships can bring in additional resources and expertise to enhance the quality of education in rural areas.